The graph of \( \text{Erf} (x) \) is presented below.
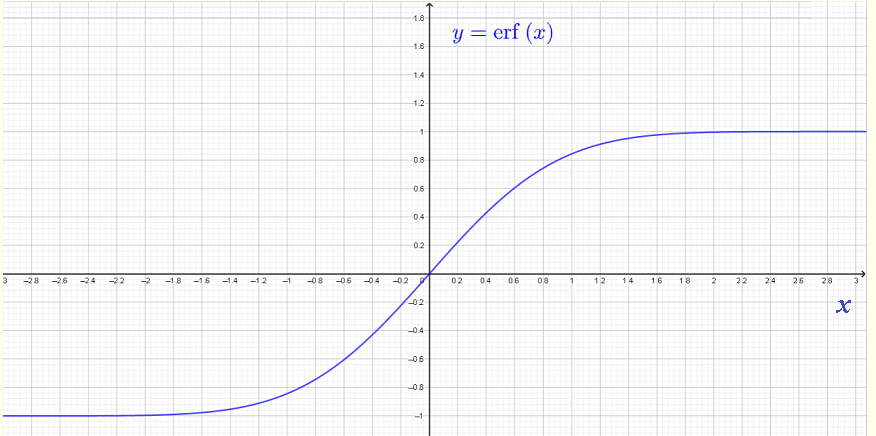 From the definition and the graph, we can say that \( \text{Erf} \; (x) \) is an odd function and therefore
From the definition and the graph, we can say that \( \text{Erf} \; (x) \) is an odd function and therefore
\( \qquad \text{Erf} \; (-x) = -\text{Erf} \; (x) \)
The error function \( \text{Erf} \; (x) \) is defined by the integral [4]
\[ \displaystyle \text{Erf} \; (x) = \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}} \int_0^{x} \; e^{-t^2} \; dt \]
Computer programs, in different languages, may easily be developed to calculate the \( \text{Erf} \; (x) \). (see for example : Error function calculator )
The graph of \( \text{Erf} (x) \) is presented below.
 From the definition and the graph, we can say that \( \text{Erf} \; (x) \) is an odd function and therefore
From the definition and the graph, we can say that \( \text{Erf} \; (x) \) is an odd function and therefore
\( \qquad \text{Erf} \; (-x) = -\text{Erf} \; (x) \)
The normal density function of a random variabe \( X \) with mean \( \mu \) and standard deviation \( \sigma \) is given by [1] [2] [3] [4].
\[ f_{X}(x) = \dfrac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2 \; \pi }} \; e^{-\frac{1}{2} \left(\dfrac{x -\mu}{\sigma} \right)^2 } \qquad (I) \]
whise graph is shown below.

The cumulative distribution function of \( f_{X}(x) \) is given by
\[ F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) = \int_{-\infty}^{x} f_{X}(t) dt \]
When \( f_{X}(t) \) is substituted by \( f_{X} \) defined in \( (I) \), we have
\[ \displaystyle F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) = \dfrac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2 \; \pi }} \int_{-\infty}^{x} \; e^{-\frac{1}{2} \left(\dfrac{t -\mu}{\sigma} \right)^2 } dt \qquad (II) \]
\( F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) \) is used to calculate the probabilities as follows
\( \qquad P( X \lt x) = F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) \)
\( \qquad P( b \le X \le a) = F_{X}(a) - F_{X}(b) \)
We now develop the relationship between the cumulative distribution function for a normal distribution defined above and given by
\[ F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) = \dfrac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2 \; \pi }} \int_{-\infty}^{x} \; e^{-\frac{1}{2} \left(\dfrac{t -\mu}{\sigma} \right)^2 } dt \qquad (III) \]
and the error function defined by
\[ \displaystyle \text{Erf} \; (x) = \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}} \int_0^{x} \; e^{-t^2} \; dt \qquad (IV) \]
Let \( z = \dfrac{t-\mu}{\sigma \sqrt 2} \) and therefore \( \dfrac{dz}{dt} = \dfrac{1}{\sigma \sqrt 2} \) or \( dz = \dfrac{1}{\sigma \sqrt 2} dt \)
Substitute the above in \( (III) \) and write
\[ \displaystyle F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) = \dfrac{1}{ \sqrt{\pi} } \int_{-\infty}^{\dfrac{x-\mu}{\sigma \sqrt 2}} \; e^{-z^2 } dz \]
Split the interval of integration and write \( F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) \) as follows
\[ \displaystyle F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) = \dfrac{1}{ \sqrt{\pi} } \left( \int_{-\infty}^{0} \; e^{-z^2 } dz + \int_{0}^{\dfrac{x-\mu}{\sigma \sqrt 2}} \; e^{-z^2 } dz \right) \qquad (V) \]
We now use the Gaussian integral Gaussian integral which is given by
\[ \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} e^{-x^2} dx = \sqrt {\pi}\]
and because \( e^{-x^2} \) is an even function, we have
\[ \int_{-\infty}^{0} e^{-x^2} dx = \int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-x^2} dx \]
Use the Gaussian integral to write
\[ \int_{-\infty}^{0} e^{-x^2} dx = \int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-x^2} dx = \dfrac{\sqrt {\pi}}{2}\]
Substitute in \( \qquad (V) \) and write
\[ \displaystyle F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) = \dfrac{1}{ \sqrt{\pi} } \left( \dfrac{\sqrt {\pi}}{2} + \int_{0}^{\dfrac{x-\mu}{\sigma \sqrt 2}} \; e^{-z^2 } dz \right) \qquad (V) \]
Using \( (IV) \) , we write \( \displaystyle \int_0^{\left(\dfrac{x - \mu}{\sigma\sqrt 2}\right)} \; e^{-t^2} \; dt = \dfrac{\sqrt{\pi}}{2} \text{Erf} \; \left(\dfrac{x - \mu}{\sigma\sqrt 2}\right) \) which we substitute in \( (V) \) above to write
\[ \displaystyle F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) = \dfrac{1}{ \sqrt{\pi} } \left( \dfrac{\sqrt {\pi}}{2} + \dfrac{\sqrt{\pi}}{2} \text{Erf} \; \left(\dfrac{x - \mu}{\sigma\sqrt 2}\right) \right) \qquad (V) \]
Simplify and write the relationship between between \( F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) \) and \( \text{Erf} \; (x) \) as follows:
\[ \boxed {\displaystyle F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) = \dfrac{1}{2 } \left( 1 + \text{Erf} \; \left(\dfrac{x - \mu}{\sigma\sqrt 2}\right) \right)} \]
Hence the normal distribution cumulative function \( F_{X}(x,\mu,\sigma) \) may be calculated using the error function \( \text{Erf} (x) \).