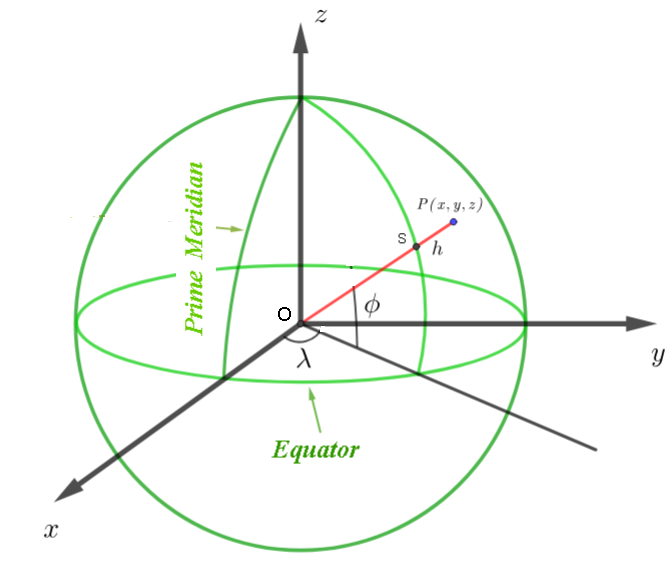
ECEF (Earth-Centered Earth-Fixed) Coordinates
A Cartesian system (X,Y,Z) with origin at Earth's center:
- X-axis: Intersection of Prime Meridian and Equator
- Y-axis: 90\(^\circ\) East longitude at Equator
- Z-axis: North Pole
Key Formulas (WGS 84 Ellipsoid)
The conversion uses the following parameters:- Semi-major axis (equatorial radius): \( a = 6,378,137 \, \text{m} \)
- Semi-minor axis (polar radius): \( b = 6,356,752.3142 \, \text{m} \)
- Flattening: \( f = \dfrac{a - b}{a} \approx 1/298.257223563 \)
- Latitude \( \phi \) (in radians)
- Longitude \( \lambda \) (in radians)
- Elevation \( h \) (meters above the ellipsoid)
-
We convert by following the steps:
- Step 1: Compute the prime vertical radius of curvature (\( N \)): \[ N = \dfrac{a}{\sqrt{1 - e^2 \sin^2 \phi}} \quad \text{where} \quad e^2 = 1 - \left(\dfrac{b}{a}\right)^2 \approx 0.00669437999014 \]
- Step 2: Calculate the Cartesian coordinates (\( X, Y, Z \)): \[ \begin{align*} X &= (N + h) \cos \phi \cos \lambda \\ Y &= (N + h) \cos \phi \sin \lambda \\ Z &= \left( N (1 - e^2) + h \right) \sin \phi \\ \end{align*} \]
Example
Example: \( 40.6892^\circ \text{N}, -74.0445^\circ \text{W}, h = 93 \, \text{m} \).- Calculate \( N \): \[ N = \dfrac{6,378,137}{\sqrt{1 - 0.00669438 \sin^2(40.6892^\circ))}} \approx 6,387,203.25 \, \text{m} \]
- Compute \( X, Y, Z \): \[ \begin{align*} X &= (6,387,203.25 + 93) \cos(40.6892^\circ) \cos(-74.0445^\circ) \approx 1,331,915 \, \text{m} \\ Y &= (6,387,203.25 + 93) \cos(40.6892^\circ) \sin(-74.0445^\circ) \approx -4,652,103 \, \text{m} \\ Z &= \left(6,387,203.25 \times (1 - 0.00669438) + 93\right) \sin(40.6892^\circ) \approx 4,164,962 \, \text{m} \\ \end{align*} \]
The ECEF coordinates are used:
- For precise global positioning (e.g., aviation, satellite orbits).
- When integrating GPS data into 3D Earth models (e.g., GIS, simulations).