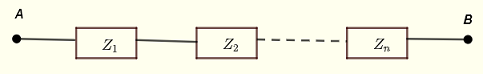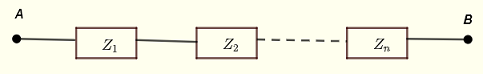The formulas for impedances grouped in series and in parallel and the formula for the impedances of basic series and parallel circuits are presented.
The impedance \( Z_{AB} \) that is equivalent to the impedances \( Z_1 \), \( Z_2 \) .... \( Z_n \) grouped in series, as shown below, is given by
\[ Z_{AB} = Z_1 + Z_2 + ... + Z_n \]
The impedance \( Z_{AB} \) that is equivalent to the impedances \( Z_1 \), \( Z_12 \) .... \( Z_n \) grouped in parallel, as shown below, is given by
\[ \dfrac{1}{Z_{AB}} = \dfrac{1}{Z_1} + \dfrac{1}{Z_2} + ... + \dfrac{1}{Z_n} \]
or
\ Z_{AB} = \dfrac{1}{ \dfrac{1}{Z_1} + \dfrac{1}{Z_2} + ... + \dfrac{1}{Z_n} } \]
| Circuit | Description | Impedance Z | Magnitude |Z| | Phase \( \theta \) |
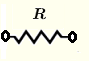
| Resistor | \( Z = R \) | \( |Z| = R \) | \( \theta = 0\) |
| | |
| | |
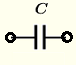
| Capacitor | \( Z = \dfrac{1}{j \omega \; C} = - \dfrac{j}{\omega \; C} \) | \( |Z| = \dfrac{1}{\omega \; C} \) | \( \theta = - 90^{\circ}\) or \( -\dfrac{\pi}{2} \) |
| | |
| | |
| Inductor | \( Z = j \omega \; L \) | \( |Z| = \omega \; L \) | \( \theta = 90^{\circ}\) or \(\dfrac{\pi}{2} \) |
| | |
| | |
| \( R \) and \( L \) in series | \( Z = R + j \omega \; L \) | \( |Z| = \sqrt{R^2 + (\omega \; L)^2} \) | \( \theta = \arctan \left(\dfrac{\omega \; L}{R}\right) \) |
| | |
| | |
| \( R \) and \( L \) in parallel | \( \dfrac{1}{Z} = \dfrac{1}{R} - j \dfrac{1}{\; \omega \; L} \)
| \( |Z| = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{R^2}+\dfrac{1}{(\omega \; L)^2}} } \) | \( \theta = \arctan \left(\dfrac{R}{\omega \; L}\right) \)
|
| | |
| | |
| \( R \) and \( C \) in series | \( Z = R - j \dfrac{1}{\omega \; C} \) | \( |Z| = \sqrt{R^2 + \dfrac{1}{(\omega \; C)^2}} \) | \( \theta = \arctan \left(\dfrac{- 1}{R \omega C}\right) \) |
| | |
| | |
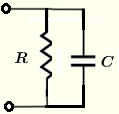
| \( R \) and \( C \) in parallel | \( \dfrac{1}{Z} = \dfrac{1}{R} + j \; \omega \; C \) | \( |Z| = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{R^2}+(\omega \; C)^2} } \) | \( \theta = - \arctan \left( R {\omega \; C}\right) \) |
| | |
| | |
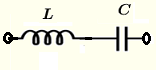
| \( L \) and \( C \) in series | \( Z = j \omega L - j \dfrac{1}{\omega \; C} \) | \( |Z| = \left| \omega L - \dfrac{1}{\omega \; C} \right| \) | \( \theta = \begin{cases} \dfrac{\pi}{2}, & \mbox{if } \omega L - \dfrac{1}{\omega\; C } \gt 0 \\ - \dfrac{\pi}{2} , & \mbox{if } \omega L - \dfrac{1}{\omega \; C} \lt 0 \\ 0 , & \mbox{if } \omega L - \dfrac{1}{\omega \; C} = 0 \end{cases} \)
|
| | |
| | |
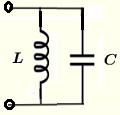
| \( L \) and \( C \) in parallel | \( \dfrac{1}{Z} = j \; \omega \; C - \dfrac{j}{ \; \omega \; L} \) | \( |Z| = \dfrac{1}{\left| \omega C - \dfrac{1}{\omega \; L} \right|} \) | \( \theta = \begin{cases} -\dfrac{\pi}{2}, & \mbox{if } \omega C - \dfrac{1}{\omega\; L} \gt 0 \\ \dfrac{\pi}{2} , & \mbox{if } \omega C - \dfrac{1}{\omega \; L} \lt 0 \\ 0, & \mbox{if } \omega C - \dfrac{1}{\omega \; L} = 0 \end{cases} \) |
| | |
| | |
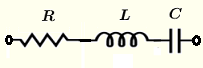
| \( R \), \( L \) and \( C \) in series | \( Z = R + j \omega \; L - j \dfrac{1}{\omega \; C}\) | \( |Z| = \sqrt{R^2 + \left(\omega \; L- \dfrac{1}{\omega \; C} \right)^2} \) | \( \theta = \arctan \left(\dfrac{\omega^2 L C - 1 }{ R \omega C}\right) \) |
| | |
| | |

| \( R \), \( L \) and \( C \) in parallel | \( \dfrac{1}{Z} = \dfrac{1}{R} + j \omega \; C - j \dfrac{1}{ \omega \; L} \) | \( |Z| = \dfrac{1} { \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{R^2} + \left(\omega \; C- \dfrac{1}{\omega \; L} \right)^2 }} \) | \( \theta = - \arctan \left(\dfrac{R(\omega^2 \; L \; C - 1) }{ \omega \; L}\right) \) |